How Is Fungal Acne Different from Bacterial Acne?
Share
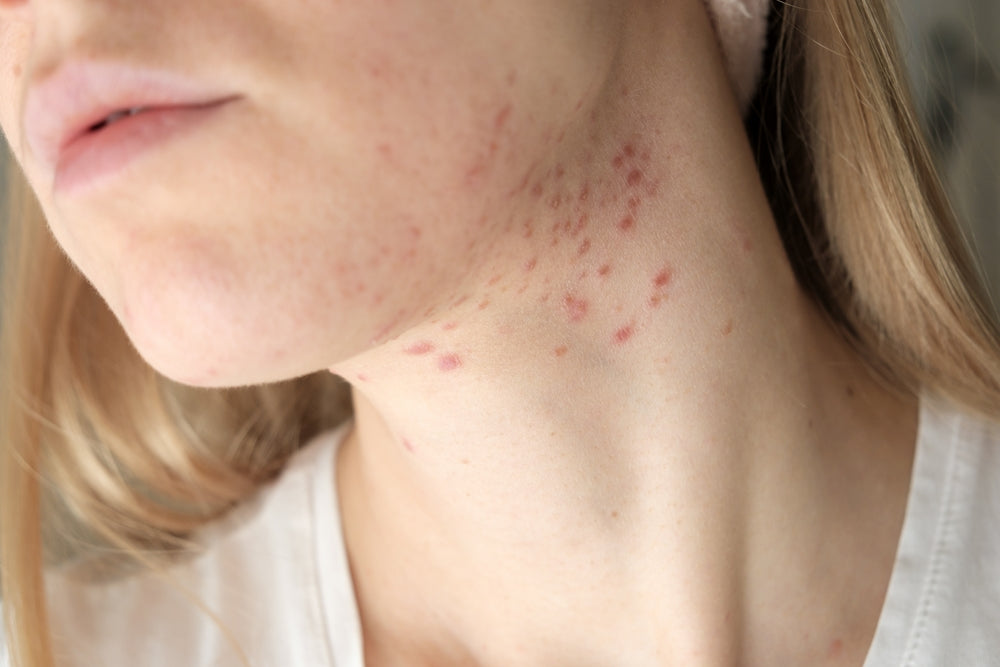
When it comes to skincare, not all acne is the same. Two common types of acne fungal and bacterial are often confused, leading to improper treatment. Understanding the differences between fungal and bacterial acne is essential for choosing the right skincare products and treatments for clear, healthy skin.
What Is Bacterial Acne?
Bacterial acne is the most familiar type of acne, characterized by pimples, whiteheads, and blackheads. This type of acne is caused by the overgrowth of the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes, which leads to clogged pores and inflammation. Factors like hormonal changes, excess oil production, and improper skincare can exacerbate bacterial acne. It typically appears on the face, chest, and back.
Bacterial acne can vary in severity, from mild breakouts to cystic acne. The good news is that bacterial acne is often responsive to over-the-counter treatments containing ingredients like salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, or topical antibiotics.
What Is Fungal Acne?
Fungal acne is caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, which naturally lives on our skin. When the balance of this yeast is disrupted, it can lead to tiny, itchy, and uniform pimples that resemble bacterial acne but feel very different. Fungal acne often occurs due to factors like high humidity, excessive sweating, or the use of skincare products that are too rich or oily. Unlike bacterial acne, fungal acne tends to cluster in areas like the upper back, chest, and shoulders.
Fungal acne is often mistaken for bacterial acne, leading to the use of products that might worsen the condition. Ingredients like oils can further fuel the growth of yeast, so antifungal treatments such as those containing ketoconazole are more effective for this type of acne.
Key Differences
Key differences in between bacterial and fungal acne are:Cause
Bacterial acne is caused by bacteria, while fungal acne is due to yeast.Appearance
Bacterial acne typically involves whiteheads, blackheads, and cysts, while fungal acne shows up as uniform, itchy bumps.Location
While both types of acne can affect the face and back, fungal acne is more common on the chest and shoulders.Treatment
Bacterial acne responds to traditional acne treatments like benzoyl peroxide, while fungal acne requires antifungal products.Treating Acne the Right Way
Understanding whether your acne is fungal or bacterial is key to treating it effectively. For bacterial acne, cleansing and using non-comedogenic products can help. For fungal acne, keeping the skin dry and opting for antifungal treatments is essential. At Ela De Pure, we offer natural skincare products that help restore balance and prevent breakouts without disrupting your skin’s microbiome.
